This resource has recently gained considerable importance for the Russian academic society . It is more than an electronic library, the platform also has a wide analytic potential. We will turn to its analytic functions next time, it is on the basics that we focus this time.
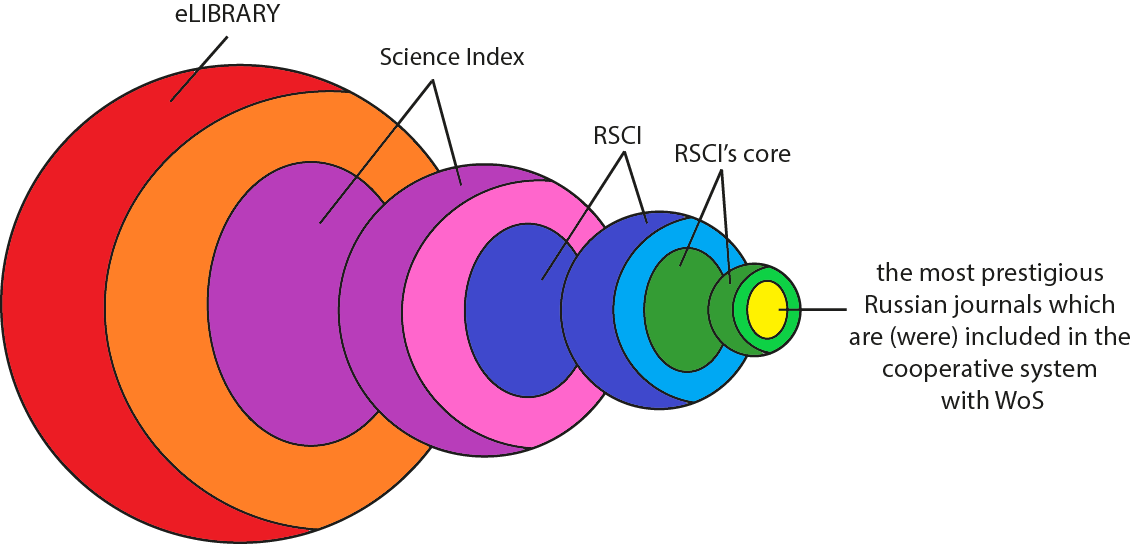
Firstly, we have to clarify the difference between the RSCI, Science Index and the library website itself. Many users regard these three systems as identical, which is not quite true.
The RSCI, Russian Science Citation Index, is the national scientometric database and the citation index, which evaluates articles’ level based on formal and objective indicators.
The main scientometric indicators of the RSCI are as follows:
- citation index;
- h-index;
- impact-factor.
The RSCI is a project created on the basis of the electronic library. This database has its own “elite” section, the RSCI’s core. When the RSCI launched cooperation with Web of Science, a separate database of articles from the most prestigious Russian journals was also formed.
Science Index is an analytical add-on in the RSCI which calculates more complex scientometric indicators than is possible in the basic interface.
What is the difference between the RSCI and HAC?
The main reason why the RSCI was created is the intention to increase the visibility of Russian research in the world academic society. Earlier, only one of ten papers by Russian scientists was included in international databases. As mentioned above, this project does not have a separate platform, its connection with the eLIBRARY is inextricable. That's why many users consider them identical.
HAC (Higher Attestation Committee) is an institution that is responsible for awarding academic degrees or titles. It also determines the criteria that articles in the RSCI have to follow . Thus, being published in a HAC journal is more difficult but also more prestigious.
The RSCI database contains more than 10 million papers from the journals that have concluded an agreement with it. Unfortunately, such a formal approach results in “garbage” journals within the selection.
Registration in eLIBRARY
Working with all the platform's services requires a profile. Unfortunately, the English version of the site is not provided.

Please note that right from the main page there are links to the most popular pages, such as the RSCI and open access journals.
If you are responsible for the eLIBRARY within the institution, you will use the "Science Index for organizations" section, which contains information about your members (authors), their papers and the reader activity.
The author's registration differs from that of the user. As an author in the Science Index system you will be provided a special author's form, which can be completed at any time.
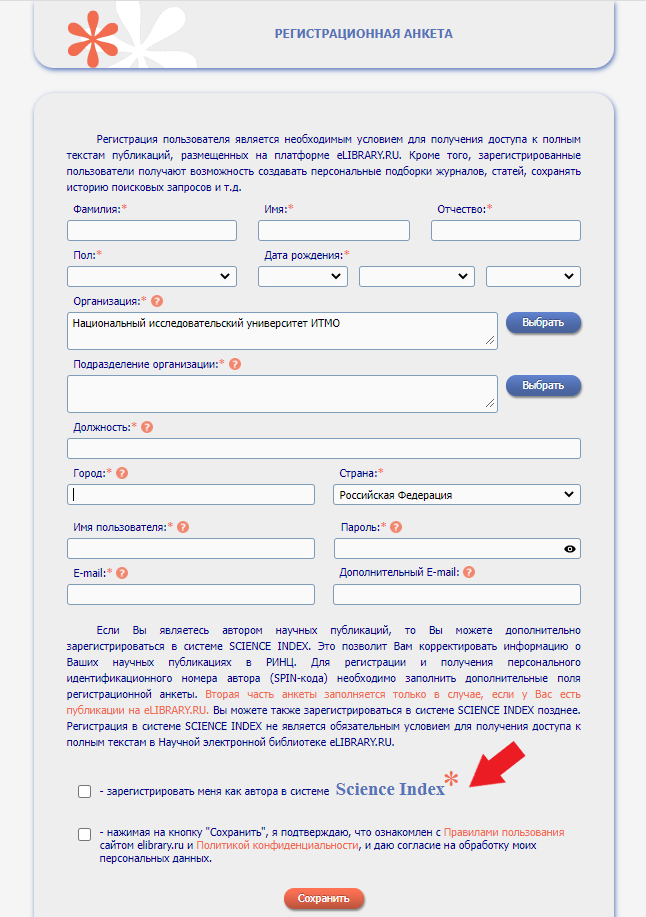
If you access the electronic library from a computer connected to the Internet on campus, the column "Organization" will be filled automatically.
Search in eLIBRARY
There are several ways to accomplish search. The most obvious is through the search field at the top of the main page.

We recommend switching to the advanced search system. A flexible system of filters is useful given the huge number of documents in the system: more than 3,000 new papers are uploaded to the platform every day.
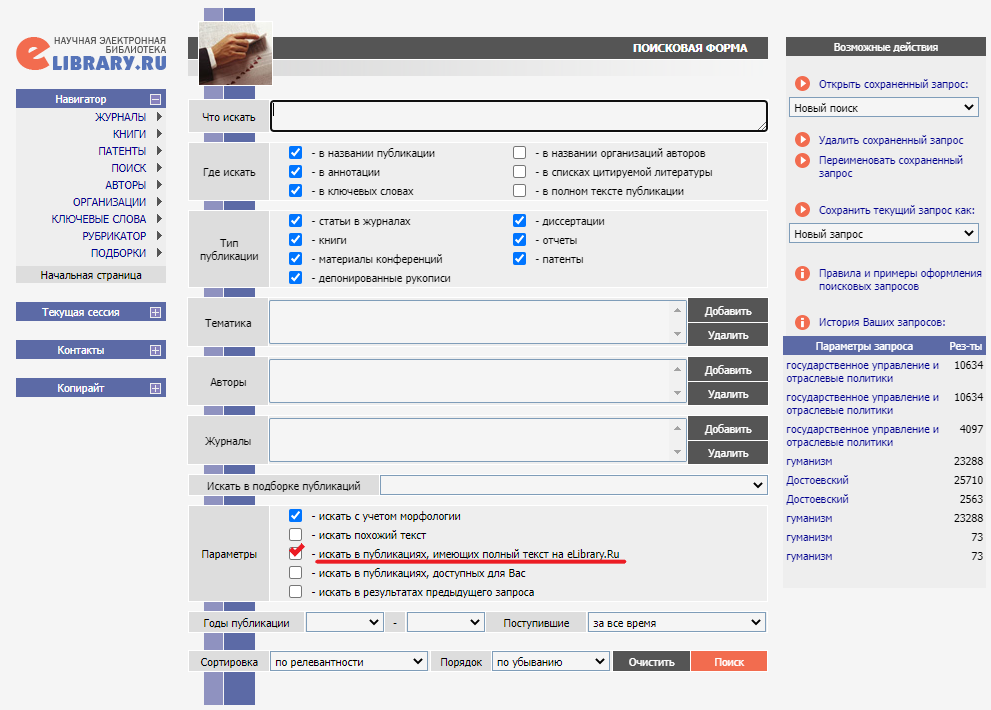
Normally, results contain a lot of data “redundant” for most users: bibliographic descriptions without PDF files or links to the full text on the source site. In order to eliminate these positions from the list, check the item “search full text papers” in the “Parameters” field. Even if you don't choose this option, the platform gives you a hint as to which positions contain access to the full text.
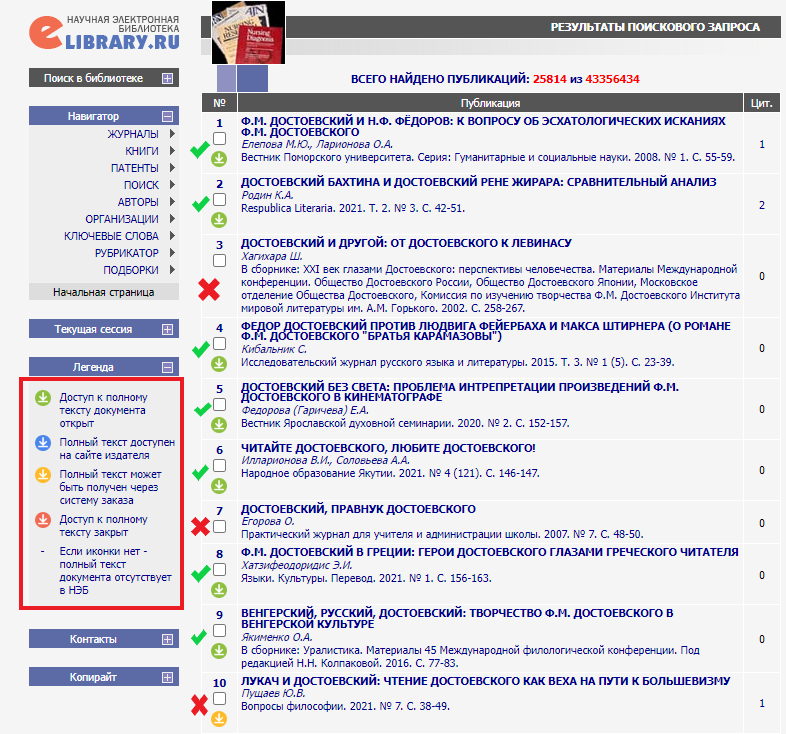
Each document has a label indicating the access depth. The left hand side of the screenshot above provides their decoding.
A gem in the treasury of the advantages of the eLIBRARY is the ability to search authors, journals, books and institutions and not only documents. There is a navigator on the right which does not disappear, even if you go on to other pages of the site.
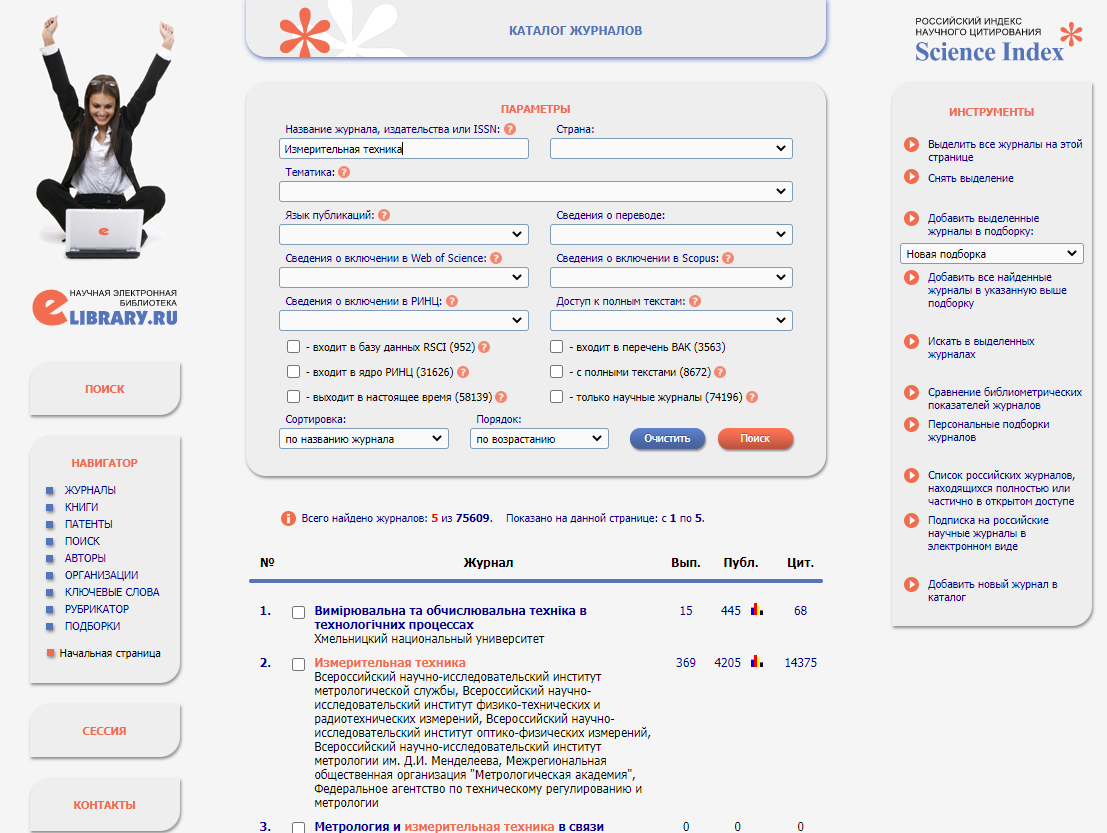
Searching through the catalog is the best option for those who select a journal for publication. The filter allows you to both select the most prestigious journals and increase the chances to find a less-known one in which your manuscript is more likely to be accepted . An ambitious project of cooperation with Scopus and Web of Science had made it possible to make sure that the selected journal was also indexed in international databases. At the moment, the above data is not updated in these systems but you can still find out whether the journal used to be indexed in Scopus or WoS earlier.
Those are the main functions and features of the eLIBRARY platform. We hope you find this information helpful!


